Intelligent Automation: The Complete Guide
Intelligent automation, also referred to as intelligent process automation or cognitive automation, is revolutionizing workflows across industries. This comprehensive guide provides an in-depth exploration of IA, offering valuable insights and practical applications.

Intelligent automation (IA), also referred to as intelligent process automation or cognitive automation, is revolutionizing workflows across industries. This comprehensive guide provides an in-depth exploration of IA, offering valuable insights and practical applications.
What is Intelligent Automation?
Intelligent Automation (IA) refers to the combination of artificial intelligence (AI) technologies with Robotic Process Automation (RPA) to automate business operations.
At its core, IA involves using machines to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as understanding natural language, recognizing patterns, making decisions, and learning from data. This integration allows businesses to automate complex processes that were previously thought to be beyond the reach of standard automation solutions.
In simple terms, the process is all about giving the robot a brain to automate the repetitive processes. Implementing IA is like having a robot that not only follows instructions but also learns from its experiences and makes decisions based on what it has learned.
Benefits of IA
The core benefits of AI include saving costs, boosting efficiency, easy scaling, and probably most importantly, removing the chance of errors. In the following sections, we'll cover some of the major benefits of implementing AI for your business.
Accuracy with less human intervention
AI, or Artificial Intelligence, is all about automating tasks while maintaining accuracy and reliability. It excels at automating processes with minimal errors. What's more, AI continuously learns, making the entire system smarter over time. With each iteration, the system becomes unparalleled, requiring little to no human intervention.
Boosting Efficiency and cutting costs
AI and RPA are already powerful enough to boost efficiency. Combining them will give you maximum benefits. It will allow your team to focus on the creative and complex challenges while IA handles all the repetitive tasks. It also allows the organization to cut expenses as the system does most of the tasks. No need to hire staff for every process.
Regulations compliance and scaling up
IA can enforce a standard process for maintaining the audits. In simple words, it automates the compliance tasks keeping the businesses compliant with the new rules. Along with maintaining the current processes, it also helps the organization to scale up whenever needed.
Use cases
There are various applications of IA. This section covers some of the top use cases popular in the industry.
- Customer Service: IA uses chatbots to answer questions anytime which helps improve support.
- Data Analysis: Finds patterns in big data to guide business decisions.
- Finance and Accounting: Speeds up invoicing and payments, and detects fraud.
- Business processes: Predicts the demand and helps in analyzing data.
- HR and Recruitment: Automates hiring tasks and tracks employee performance.
- Manufacturing: Monitors equipment and controls robots for efficiency.
- Marketing: Personalizes campaigns and measures their success in real-time.
How does it work? Which approaches are used?
Intelligent Automation works by combining the power of Artificial Intelligence (AI) along with Robotic Process Automation (RPA).
AI: AI aims to create software or machines that can think and learn like a human. It includes decision-making and learning from the previously fed data.
RPA: RPA is a process of creating robots or bots to mimic a human action. The bots are capable of doing small tasks like automating an email and are even used for complex tasks.
IA utilities both of these concrete technologies to provide the ultimate result that requires less to no human intervention. To attain these results, there are various AI and RPA subsets used. Below are some of the approaches used to achieve Intelligent Automation.
Machine Learning
Machine learning is a part of AI where an algorithm is used to train the machine from the data without explicitly programming it. Streaming services like Netflix use ML to suggest new web series or movies based on what you have already watched.
Natural Language Processing
NLP is a process of teaching computers a human language to understand and produce outcomes. It’s widely used in chatbots. Another good example here could be Siri where you can ask any question and it gives output in a human language.
Computer Vision
Computer Vision involves enabling systems to identify and interpret visual information, such as recognizing objects and faces. For instance, in document processing, Computer Vision can extract data from invoices or receipts, automating tasks like expense tracking.
Optical Character Recognition
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) enables systems to recognize and interpret text within images or files. This technology is employed in intelligent automation to extract data from documents. It finds extensive application in banking for cheque processing and in educational institutions for grading exam papers.
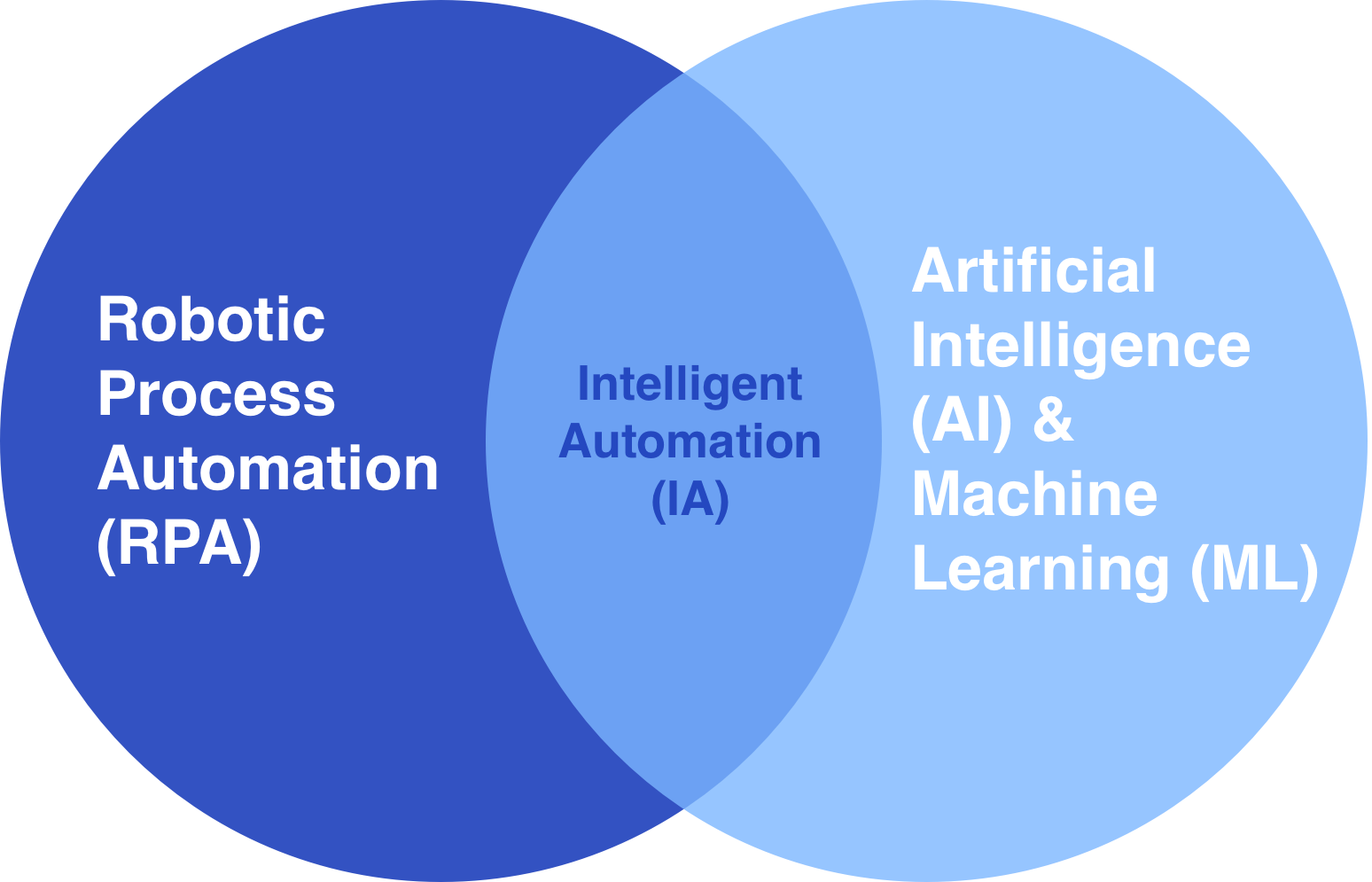
Intelligent Automation (IA) vs. Robotic Process Automation (RPA): What's the Difference?
While both Intelligent Automation (IA) and Robotic Process Automation (RPA) are transformative technologies aimed at streamlining operations, they serve distinct purposes.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) focuses on automating repetitive, rules-based tasks. It operates by mimicking human actions within digital systems, executing tasks efficiently and error-free.
On the other hand, Intelligent Automation (IA) encompasses a broader spectrum of automation technologies, including artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). IA not only automates routine tasks but also leverages cognitive capabilities to analyze data, make decisions, and adapt to dynamic environments.
In essence, RPA is the foundation of IA, providing the automation backbone, while IA extends the capabilities by integrating cognitive technologies for enhanced decision-making and problem-solving. Depending on the complexity and requirements of your processes, you may choose either RPA for repetitive tasks or IA for more advanced automation needs.
The future of IA
The future of IA looks bright as more and more businesses are implementing IA in their operations. In the coming years, more and more small businesses will be able to utilize IA for automating their business processes.
According to SS&C Blue Prism, one can see increase in IA implementation in the following areas:
- Generative AI + intelligent automation.
- Digital worker-first processes.
- Evolving from pure play to platform play.
- Strategic applications.
- Better user accessibility for developers.
- Ethical automation and ESG compliance.
- Governance and security.

